Whenever I do something that causes the screen to turn off during a call, that includes putting the phone up to my ear to speak, the call would become very choppy and it would eventually disconnect from Skype completely. I have found a fix for this, and I’d like to share it with you so I can help others that may be having the same problem.
This post is the written version of my video tutorial, which you can watch below. The fix in the video is the same as it is here, but the video walks you through it in video form and also demonstrates the problem before and after fixing.
So, I will explain the process of this fix, and post images that will walk you through it. It’s really a very easy fix.
Before we jump into how to fix it, you need to know that the option used in this fix is not available on all ROMs. On the stock ROM for the HTC Evo 4G, I don’t think I saw this option. To find ROMs for your phone, go to http://forum.xda-developers.com/
Also the fix isn’t perfect. Yes, even after the fix, it may still be choppy for a few seconds on turning the screen off. But after that initial choppiness the call is smooth and sounds good, and most importantly it won’t disconnect. (Unless your Internet connection is bad)
So now, onto the fix!
This fix is actually ridiculously easy to do. Most of the video tutorial was just demonstrating the problem, and then the result of the fix.
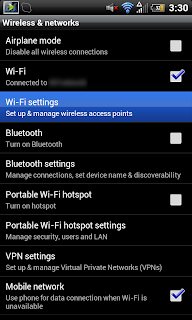
First, open your settings menu. You can do this by pressing the “menu” button alongside your home, search and back buttons. Or, you can go into your applications and look for Settings.
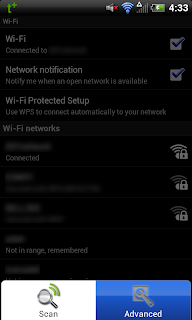
Next, check the box that says “Best Wifi Performance”. This part is critical, and unfortunately the option may not be available on all phones/ROMs.
Now, if you make a call with Skype and the screen is turned off during the call either by the sleep button or holding the phone up to your ear, the call won’t be dropped.
If a menu option shown here was missing on your device:
I’ve only ever used one Android device, and that’s my HTC Evo 4G. I can’t say anything for sure about other devices, but I know that at least on mine, the solution is to try another ROM. Other devices may not have this option at all on any ROM, other devices might not even have this problem to begin with. But, the only advice I can give you is to try another ROM. I can’t help you any more than that as far as missing menu options goes.
To find ROMs for your device, go to the XDA forums here: http://forum.xda-developers.com/
My ROM is called Energy, you can find it here: http://bit.ly/wmkS9c
Thanks for reading, I hope this helped you. Please comment if you have a question, suggestion, or comment on my post!